What is Cancer?
The body is made up of cells which grow and die in a controlled way. Sometimes, cells keep on growing without control, causing an abnormal growth called a tumour. A tumour can be benign (harmless). premalignant (if left untreated, may lead to cancer) or malignant (progressively worsen and can result in death).
Cancer is a malignant tumour.
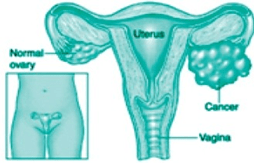
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovaries are a pair of oval shaped reproductive organs present on either side of the uterus in which female eggs are produced. Ovarian cancer occurs when the normal ovarian cells begin to grow in an uncontrolled, abnormal manner and produce tumors in one or both the ovaries.
What are the Possible Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer?
The exact cause of ovarian cancer remains unknown, yet certain factors are linked to the chance of getting the disease.
Below Mentioned are the Factors that are Known to Increase the Risk of Ovarian Cancer in Women
- Age: The risk is more as a woman gets older. Most cases are diagnosed in women following the menopause
- Genetic risk factors: Damage to certain genes (due to inherited or environmental changes) increases the risk.
- Family history: Risk is higher among women whose dose blood relatives (either from mother's or father's side) of the family have this disease. History of the breast, uterus, colon, or rectum cancer in the family also increases the risk.
- Weight: Being overweight or obese increases the risk.
- HRT: Using hormone replacement therapy, particularly estrogen-only HRT for 5-10 years can increase a woman's risk.
- Smoking: Women who smoke are at higher risk
Below Mentioned are the Factors that are Known to Reduce the Risk of Ovarian Cancer in Women
- Pregnancy: Women who have been pregnant and carried it to term have a lower risk than women who have not.
- Breastfeeding: Breastfeeding may lower the risk.
- Oral contraceptives: Taking oral contraceptives for more than 5 years significantly reduces the risk.
What are the Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer?
Most of the times, ovarian cancer symptoms are vague & non-specific which means it is difficult to detect early. The main symptoms are as follows:
- Abdominal pressure
- Low back pain
- Lower abdominal discomfort or pain
- Low back pain
- Lower abdominal discomfort or pain
- Unexplained changes in bowel habits, including diarrhea or constipation
- Loss of appetite
- Changes in the bladder habits including a frequent need to urinate
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Persistent lack of energy
- Pain during sex
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
How is Ovarian Cancer Diagnosed?
There are some general and some specific tests that need to be done to diagnose and confirm ovarian cancer such as physical examination, blood tests(CA-125), ultrasound, CT scans, MRI, laparoscopy, biopsy (viewing under a microscope), etc.
The doctor will decide which tests are necessary; all of them may not be done.
What are the Treatment Options for Ovarian Cancer?
Various therapies are used for the treatment of ovarian cancer for e.g. removal of tumour (surgery), killing cancer cells with drugs (chemotherapy) or radiation (radiotherapy). Depending on the size and spread of the cancer, treatment can include any of these therapies or a combination. The doctor will decide on the treatment depending on the type and severity of the disease and the condition of the patient.
How Can the Risk of Ovarian Cancer be Reduced?
The risk of ovarian cancer can be reduced by:
- Regular checkups: Getting the necessary exams and checkups done regularly, especially in those who have a family history or relatives with ovarian cancer.
- Tubal ligation: The fallopian tubes are blocked or tied.
- Hysterectomy: Surgical removal of the uterus.
- Oophorectomy: Surgical removal of one or both the ovaries for women at high risk.
- Diet: Eating healthy balanced diet with more fruits, vegetables, whole grain food.
- Weight: Achieving/maintaining desirable weight.
- Exercise & being active: Improves physical& emotional health and reduces stress
- Birth control pills: Having used birth control pills for more than five years.
- Smoking: Avoiding or quitting smoking
- Environmental factors: Reducing or avoiding exposure to carcinogens (cancer-causing agents) like radiation, talcum powder, asbestos etc.
Do’s and Don’ts
Do’s
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Regular checkups
- Eating a balanced diet
Don’ts
- Smoke
- Be overweight or obese
- Ignore symptoms
In case of any symptoms along with evidence of risk factors, please consult your doctor.