To investigate the renal effects of allopurinol treatment in hyperuricemic patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD)
Use of Allopurinol in Slowing the Progression of Renal Disease
Aim
Methods
Inclusion
1. Presence of renal disease, defined as daily proteinuria >0.5 g and/or an elevated serum creatinine (Cr) level >1.35 mg/dL (>120 mol/L) at baseline;
2. Baseline serum Cr level and daily proteinuria had not increased by >40% within the 3 months before screening
Treatment Protocol
Treatment group n=25
Depending on baseline renal function, allopurinol -
- 200 mg/d was started, if serum Cr <1.70 mg/dL
- 100 mg/d was started, if serum Cr >1.70 mg/dL
Dosages of antihypertensive drugs, lipid-lowering agents, and steroid or cytotoxic drugs were continued and adjusted according to the individual patient's clinical conditions.
Follow-up
Patients were checked for BP, Fasting uric acid, Serum Cr, Daily urinary protein excretion, Hematological parameters, every 4 weeks for the first 6 months and then every 8 weeks, for a total of 12 months.
Results
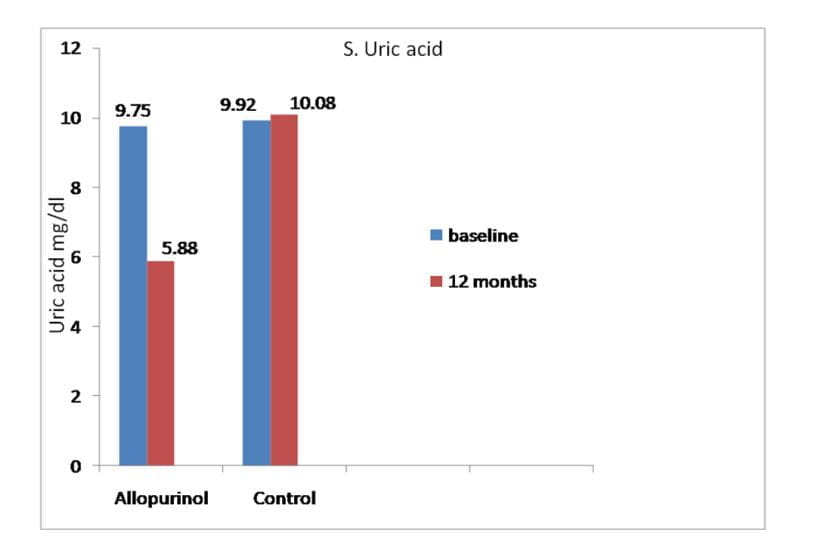
Biochemical Parameter
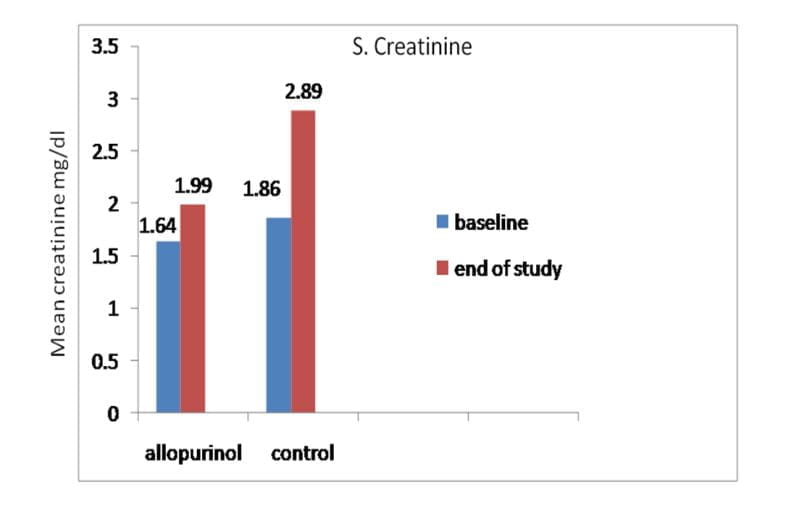
Renal Function
No significant change in serum Cr levels after 12 months in the treatment group. In the control group, there was worsening of renal function by the end of the study
Proteinuria
Baseline protein excretion was similar in both groups at the end of the study.
Haematologic Parameters
No changes in serum ALT, Lipid profile, CRP, Hb or WBC and platelet counts after 12 months.
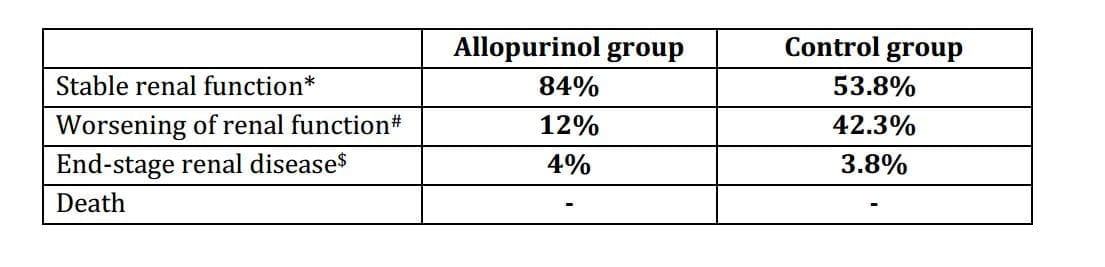
Study Endpoint Outcome
* - serum Cr level at the end of study that increased by <40% compared with baseline
Significantly (P =0.015) more patients in the control group showed deterioration in kidney function at the end of the study.
Conclusion
Allopurinol Therapy
- Significantly decreases S. uric acid levels in hyperuricemic patients with mild to moderate CKD
- Is safe and helps preserve kidney function during 12 months of therapy compared with controls
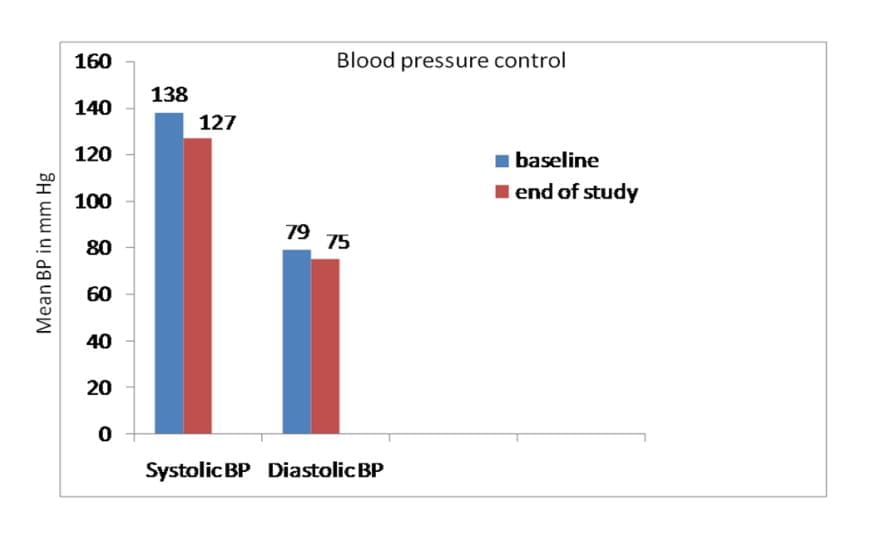
- May be necessary earlier to ameliorate the hypertensive effect of hyperuricemia
Using allopurinol to decrease serum uric acid levels is safe and may be beneficial in decreasing systolic BP and slowing the rate of deterioration in renal function