DASISION Trial: 5-Year Efficacy and Safety of Dasatinib Versus Imatinib in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Chronic Phase CML
Introduction
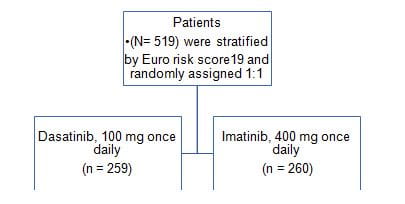
The Dasatinib Versus Imatinib Study in Treatment- Naive Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients (DASISION) study was a randomized phase III trial comparing the efficacy and safety of dasatinib with imatinib in patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in chronic phase (CP).
Aim
To report the 5-year analysis from the phase III DASISION trial, evaluating long-term efficacy and safety outcomes of patients with CML in CP treated with dasatinib or imatinib.
Patients Profile
Patients with newly diagnosed CML-CP
- Untreated CML-CP
- No pleural effusion or uncontrolled cardiovascular disease
Study Design
Study Endpoints
- The primary end point was confirmed complete cytogenetic response (cCCyR) rate by 12 months
- Secondary end points were overall time to cCCyR and its duration, major molecular response (MMR) rate at any time, time to MMR overall, PFS, and OS
Results
After 5 years, 61% of dasatinib-treated patients and 63% of imatinib-treated patients were still on initial therapy
|
Status |
No of Patients (%) | |
|
Dasatinib 100 mg Once Daily (n = 258) |
Imatinib 400 mg Once Daily (n = 258) | |
|
On initial therapy at study end Discontinued |
158 (61) |
162 (63) |
|
Progression or treatment failure |
28 (11) |
36 (14) |
|
Intolerance* |
42 (16) |
17 (7) |
|
AE unrelated to study treatment |
12 (5) |
4 (2) |
|
Poor compliance/nonadherence |
1 (1) |
7 (3) |
|
Patient request |
4 (2) |
10 (4) |
|
Withdrawal of consent |
4 (2) |
3 (1) |
|
Lost to follow-up |
1 (, 1) |
2 (1) |
|
Other |
8 (3) † |
16 (6) ‡ |
Abbreviation: AE, adverse event.
*As decided by investigator. Intolerance is defined as recurrent grade $ 3 hematologic toxicity or grade > 2 nonhematologic toxicity requiring discontinuation despite dose reduction.
†Includes insufficient molecular response (n = 3), pregnancy (n = 2), loss of complete cytogenetic response (n = 1), increased BCR-ABL1 (n = 1), and relocation to the United States (n = 1).
‡Includes no molecular response/loss of molecular response (n = 4), suboptimal response (n = 3), insufficient cytogenetic response (n = 2), investigator request (n = 2), pregnancy (n = 1), recurrence of blasts in bone marrow(n = 1), no complete molecular response (n = 1), no major molecular response (n = 1), and appearance of mutation (n = 1).
Efficacy Analysis
- Transformations to both accelerated and blast phase CML on study or after discontinuation: dasatinib, 4.6%; imatinib, 7.3%
- A higher percentage of dasatinib treated patients achieved BCR-ABL1<10% (IS) at 3 months
- 84% in dasatinib arm
- 64% in imatinib arm
- In both arms, patients who achieved BCR-ABL1 <10% (IS) at 3 months more often reached CCyR, MMR, andMR4.5 by 5 years had higher rates of OS and PFS and had a lower transformation rate (3% v 14% to 15% in patients who did not achieve BCR-ABL1 < 10% at 3 months)
|
Response |
% of Patients |
||||
|
Dasatinib 100 mg Once Daily (n = 259) |
Imatinib 400 mg Once Daily (n = 260) |
||||
|
3-Month BCR-ABL1 Transcript Level < 10% (n = 198; 84%) |
3-Month BCR-ABL1 Transcript Level > 10% (n = 37; 16%) |
3-Month BCR-ABL1 Transcript Level < 10% (n = 154; 64%) |
3-Month BCR-ABL1 Transcript Level >10% (n = 85; 36%) |
||
|
Complete cytogenetic response |
94 |
41 |
92 |
59 |
|
|
Major molecular response |
87 |
38 |
81 |
41 |
|
|
MR4.5 |
54 |
5 |
48 |
12 |
|
- Mutations were identified in 15 patients in dasatinib arm and 19 patients in imatinib arms
- T315I mutations were identified in eight dasatinib-treated patients and no imatinib-treated patients
Safety Analysis
- The safety profile for dasatinib remains consistent, with no new safety signals identified after 5 years
- Overall, most AEs reported with both drugs were grade 1 or 2; 15% of AEs reported with dasatinib and 11% of AEs reported with imatinib were grade 3 or 4
- Drug-related pleural effusion was more common with dasatinib (28%) than with imatinib (0.8%)
- First occurrences of pleural effusion were reported with dasatinib, with the highest incidence in year 1
- Arterial ischemic events were uncommon in both treatment arms
Conclusion
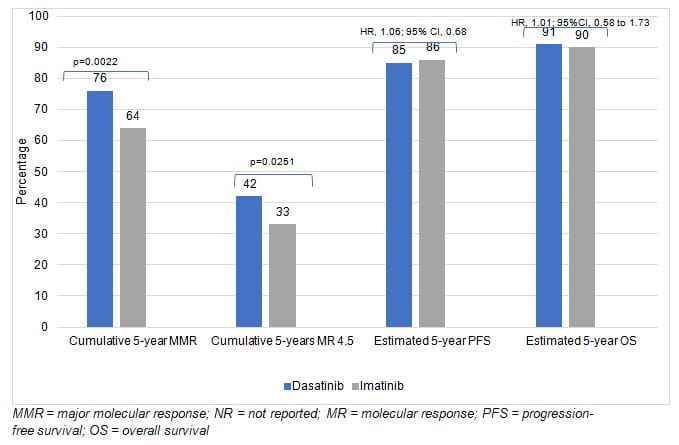
- The 5-year long-term results from DASISION demonstrated that patients taking dasatinib had faster and deeper MRs than patients taking imatinib
- The study results confirm that dasatinib treated patients have high MR rates and that the achievement of BCR-ABL1< 10% (IS) at 3 months is predictive of significantly higher PFS and OS rates
- No new safety signals observed with dasatinib through 5 years or with longer follow-up
- These results suggest that first-line dasatinib should continue to be considered a standard first-line therapy for patients with newly diagnosed CML-CP
Reference
J Clin Oncol 34:2333-2340