Introduction
Although the vaccines have been effective in preventing the COVID-19 occurrences, there is still a need for potential treatment approaches that can sterilise the virus in clusters of infected patients. Monoclonal antibodies have been effective and safe in the treatment of viral infections. Monoclonal antibodies casirivimab and imdevimab, have been approved by various organizations for ceasing the progression of COVID-19 and indicated for high-risk individuals. This combination has gained worldwide attention in developing countries.
Aim
This study assesses the efficacy and safety of Casirivimab and Imdevimab antibody cocktail in the high-risk population among symptomatic COVID-19 patients.
Method
Study Design
- Retro-prospective comparative observational study.
Patient Profile
- Individuals >18 years with confirmed diagnosis of Covid-19
- Onset of Covid-19 symptoms within 10 days
- Oxygen saturation >93%
Treatment Strategy
- Through an extensive data retrieval for 6 months, a total of 152 samples were documented and sorted into 2 subsets
- Test group comprising Casirivimab and Imdevimab treated patients (n = 79)
- Control group comprising non-Casirivimab and Imdevimab treated individuals (n = 73).
- Demographics, comorbidities, disease severity, mechanical ventilation, high flow oxygen requirement and mortality were documented.
- The phase 2 involved taking the patients’ feedback post-Covid-19, which included treatment satisfaction, vaccination status, health status, adverse drug reactions and re-hospitalization.
Endpoints
- Need for mechanical ventilation
- High flow oxygen requirement
- Mortality
Results
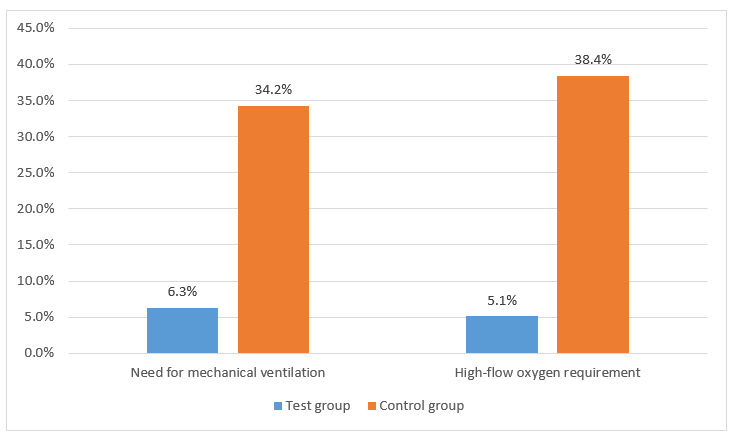
- The need for mechanical ventilation and high-flow oxygen was higher in the control group as compared to test group as seen in Figure 1; (p<0.001 for both).
- There were no deaths in the test group while there were 5 deaths in the control group.
- The non-vaccinated test group did not require mechanical ventilation as compared to 34.8% in the non-vaccinated controls.
- The high-flow oxygen requirement was lower in the test group in the individuals who were fully immunized as compared to their counterparts (6.3% vs 41.9%, p<0.01).
- The comparison of the post COVID19 feedbacks has been shown in Figure 2.
- The post-Covid difficulties reported by both subsets were hematemesis, pneumonia, shortness of breath, hair loss, dyspnea and weakness.
- None of the patients reported any significant adverse drug reaction.
Conclusion
- Casirivimab and Imdevimab antibody cocktail resulted in lesser requirement of mechanical ventilation and high-flow oxygen with no deaths as compared to the controls in symptomatic Covid-19 patients.
- The non-vaccinated patients who received this antibody cocktail did not require mechanical ventilation and those who were fully immunized seldom entailed high-flow oxygen.
- Casirivimab and Imdevimab treatment regimen is clinically beneficial for high risk COVID19 patients.
Clin Epidemiol Glob Health. Mar-Apr 2022;14:100967. Doi: 10.1016/j.cegh.2022.100967.


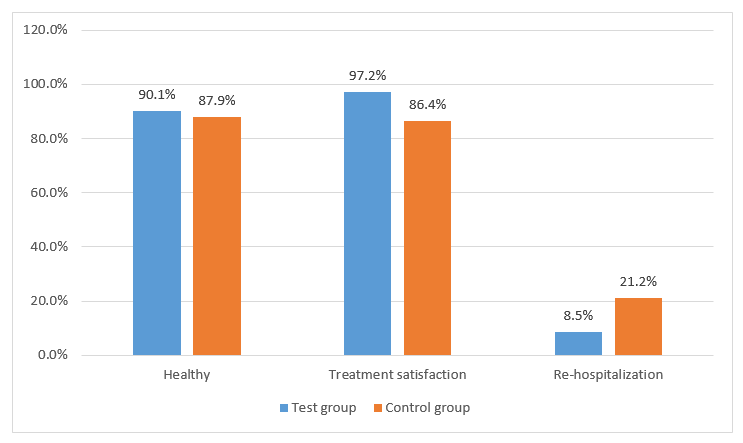







.webp?updated=20240527063817)