Benefits of Initial Combination Therapy of Vildagliptin/Metformin in Asian T2DM Patients
30 Nov, 17
Background
Evidence on effectiveness of dual combination therapy in newly diagnosed type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients, especially with high baseline glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and presence of cardiovascular (CV) risk factors is limited.
Aim
Initial combiNation therapy with vildagliptin/metformin In drug na?ve T2DM patients In a reAl Life setting (INITIAL) aimed at assessing the effectiveness of initial combination therapy with vildagliptin/ metformin in drug-na?ve T2DM patients. The study also determined the influence of age, obesity and other co-morbidities at baseline on the HbA1c reduction.
Patient Profile
- Drug-na?ve T2DM patients (n=532) aged at least 18 years with an HbA1c ≥ 7.5% (>8% in India).
Method
Study Design
- A multicentre, prospective, observational study conducted in four Asian countries, including India
Treatment Strategy
- The combination of vildagliptin/metformin was added in newly diagnosed, drug-na?ve T2DM patients.
Duration
- 24 weeks
Outcomes
Primary Outcome
- Change in HbA1c from baseline to week 24
Secondary Outcomes
- Proportion of patients achieving glycaemic target of HbA1c ≤7% at weeks 12 and 24
- Change in blood glucose levels and body weight
- Overall safety
- HbA1c reductions across the subgroups of age, body mass index (BMI) and associated comorbidities
Results
- Patients enrolled in this study were relatively young (mean age; 49.6 years), had high HbA1c at diagnosis (mean HbA1c; 9.3%) and were associated with multiple CV risk factors [dyslipidemia (30.1%), hypertension (29.7%), and obesity (20.9%)] at baseline when compared to a western population.
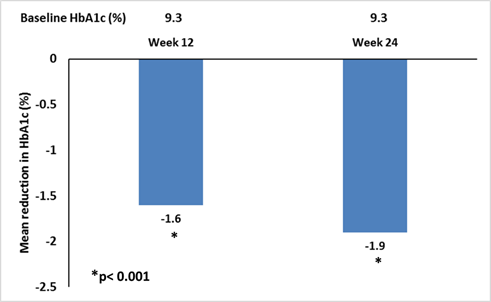
- Combination therapy with vildagliptin/metformin resulted in significant reductions in HbA1c from baseline to week 12 and this was sustained till week 24 (Figure 1)
Figure 1: Mean reduction in HbA1c from baseline to week 12 and 24
- Almost 40% of patients achieved HbA1c ≤7% goal by week 24
- Combination therapy also resulted in significant reduction in FPG (50.4 mg/dL) and PPG (81 mg/dL) at 24 weeks
- The mean change in body weight was −1.1 kg from baseline to week 24.
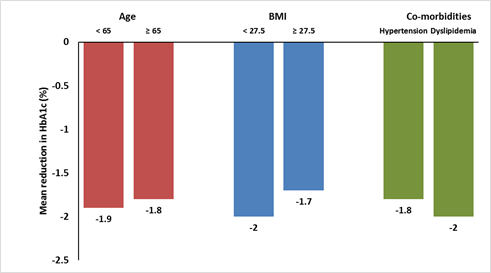
- Reductions in HbA1c from baseline to week 24 were observed across the subgroups of patients (Figure 2), irrespective of age (<65 years vs. ≥65 years), obesity (<27.5 kg/m2 vs. ≥27.5 kg/m2), or presence of co-morbidities (hypertension and dyslipidaemia).
Figure 2: Mean reduction in HbA1c stratified by subgroups
- Overall, the combination therapy was well tolerated with a safety profile consistent with that reported in previous studies.
Conclusions
- In real-world settings, the combination therapy of vildagliptin/metformin was associated with clinically meaningful and consistent reductions in HbA1c.
- This reduction was consistent across the subgroups, regardless of age, BMI, and co-morbidities such as hypertension and dyslipidaemia.
Poster 774; Presented at the 53rd European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Annual Meeting, 11–15 September 2017, Lisbon, Portugal
Related Topics